According to Failory, 9 out of 10 startups fail, and 20% fail until the end of the 1st year. In 34% of cases, the reason for failure is the lack of product-market fit. An IT company can spend years studying software and invest thousands of dollars in its development but get zero consumer demand. Often it happens, because the startup companies are trying to introduce their project quicker, and so they neglect the most important step, namely, the check for demand, which is MVP development. So what is it, and how does it help a business succeed?
THE CONCEPT OF AN MVP: WHAT IS IT, AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
A minimum vibrant product, or MVP, is a test version of a software/service which has a limited set of functions. The concept appeared as a philosophy of the Lean movement (lean manufacturing). The term was introduced by Frank Robins in 2001 and further popularized by Eric Ries into ''Lean Startup''. This movement aimed at eliminating all kinds of losses - any actions that consume resources but do not create value for the consumer.
Not surprisingly, an MVP implies minimal functionality. Even one product feature is considered to be enough to demonstrate its value, provided that this feature is key for the consumer. The specific feature of the MVP approach is that the program is still in development and can be released to the market only months later. The purpose is to get feedback from potential customers and, on this basis, assess the demand for the idea on the market.
Based on the feedback of the first users, it is possible to evaluate whether it is worth continuing the process or whether it is better to change the direction to a more popular and profitable one. Testing software at the initial stage allows us to reduce costs, as well as to ensure profit in the long term.
DIRECT AND INDIRECT FINANCIAL ADVANTAGES OF AN MVP:
- Receiving the first profit before the creation and full launch of the project.
- Forming a base of potential customers and early adopters ready to buy the product after its release.
- Attracting investors for whom the beta version became a kind of presentation of the project and helped make sure it was in demand.
- Reduction of costs for the analysis of the market situation and study of the target audience.
A common mistake is to consider an MVP to be only a product. It is a process, a mini-experiment, which helps to quickly and cost-effectively test the viability of almost any hypothesis. Within the framework of the concept, this hypothesis is a business idea, whether it is the preparation of another IT project, the creation of an additional direction, or the opening of a new company.
TYPES OF MINIMUM VIABLE PRODUCTS WITH EXAMPLES FROM THE WORLD PRACTICE
There are different ways to get feedback. The choice depends on many factors: the type of the project, peculiarities of the target audience, needs, and financial possibilities of the company. For example, if the goal is to motivate a customer to buy before the product is launched, this is called an MVP pre-order. If it is necessary to study customer needs from scratch, it's a customer-engagement MVP. Overall, there are the four most popular types.
TOP 4 OF MVP TYPES:
- Wizard Of Oz — it is an illusion that a product exists. Startup gives the impression that there's a ready service with full functionality. Users do not know that, in reality, it is a person, not a program, that performs their tasks. Example: The founder of the online store Zappos initially published photos of shoes from nearby stores on the website. When one made an order, he bought the shoes himself and sent them to the customer.
- Concierge — it is a personal communication of the startup company founder with consumers, which involves "manually" helping. The difference from the previous type is that the users know that their issues are solved by a person. Example: employees of Wealthfront, a financial planning service, at the early stage of development directly provided help to clients on money management.
- Piecemeal — it is a collection of services and tools that exist on the market and is successful. A startup doesn't build its own infrastructure but uses the achievements of other companies until it decides to scale. Example: In the beginning, Groupon consisted of 3 parts, each of which solved a specific task: WordPress (content posting), AppleScript (generating PDF sentences), and Apple Mail (sending offers).
- Single Featured — it is a demonstration of a product with a single but most important feature. This narrows the target audience, gives an idea of whether the consumer is happy, and saves money. Example: in the early stages, Spotify developers uploaded music from their PCs into the program and occasionally played it to make sure there were no stream failures. Then usability and design took a back seat - the goal was to introduce streaming technology to the target audience.
These types of MVPs differ only in implementation methods, timeframes, and money costs, but their goal is the same - to check how the product meets the requirements of the audience and in what direction it should move.
FEATURES OF AN MVP PROJECT DEVELOPMENT AND MANAGEMENT
Do you know what the main difference between demanded and non-demanded products is - that the idea was initially attainable? Also, the developers had a plan. Checking an idea comes in 9 steps, which can be divided into preparatory and basic. Important questions about the product need to be answered first, and only then do you choose the approach to create and manage.
PREPARATION FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF MVP:
- Formulating a hypothesis: for what purpose is the product being created?
- Study of the target audience and make up a portrait of the user: who is the ultimate user?
- Analysis of competitors: who is the industry leader, what market share does it have, and what strategy is it pursuing? Tip: You can find out all about your competitors' websites and applications using special services, such as Quantcast, Ahrefs, Similar Web, AppFollow, and App Annie.
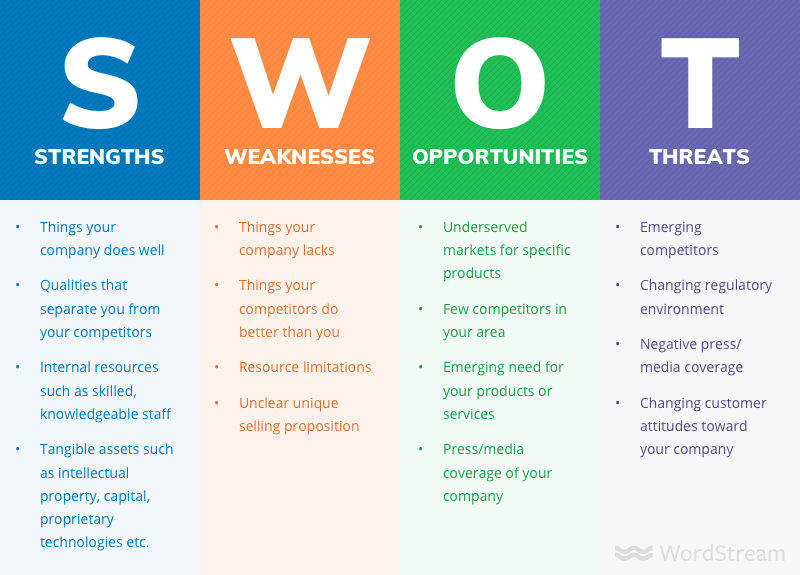
- SWOT analysis: what are your company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats?
- Making a User flow: what steps should a consumer take to benefit from your offer?
- Prioritizing features: which features are important to the consumer at each stage of the User flow?
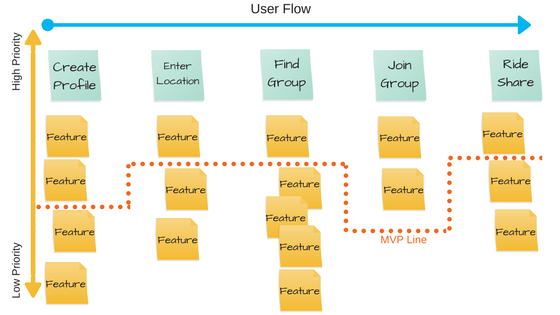
Building the framework: what are the top features you should include in the minimum set?
MVP: DEVELOPMENT AND MANAGEMENT
- Choice of method: how can you create a minimum viable product faster and more efficiently?
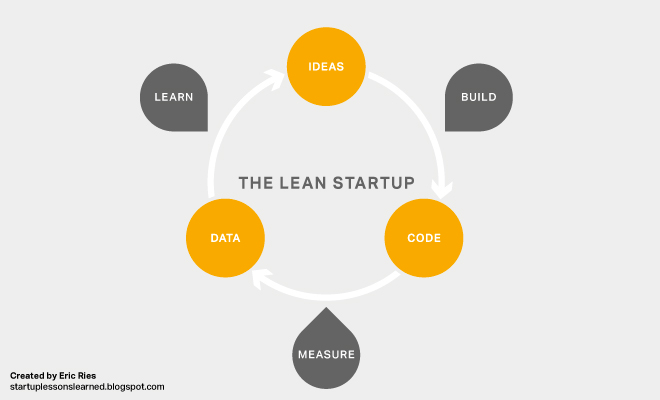
- Lean — is one of the methods of Agile software development. Works on principle: build - measure - learn. It is suitable for quick feedback and in situations where you need to postpone deciding on the project.
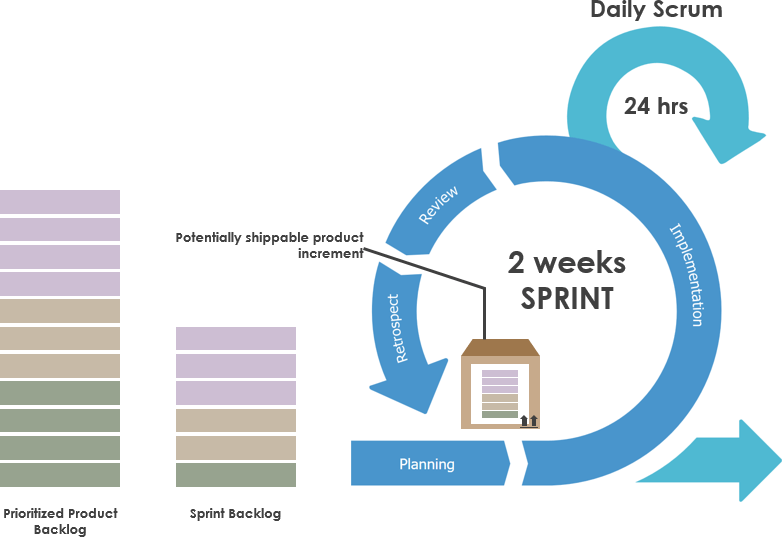
- Scrum — is a method of distributing the amount of work to increase the speed of performance. The process is divided into sprints (cycles of 2-4 weeks). A beta version is created in the first sprint and updated in the following ones based on user feedback. It is suitable for gradual and long-term improvement.
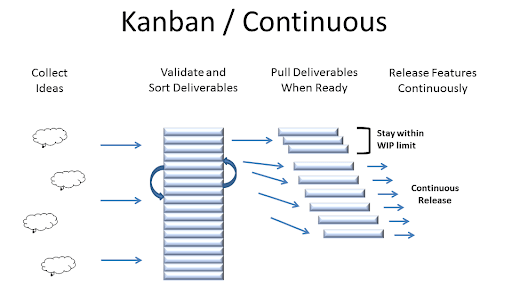
- Kanban — is a method based on the work-in-progress model. Tasks are solved as they arise, allowing an optimized workload. This approach can be used after the first product release when feedback continues to flow.
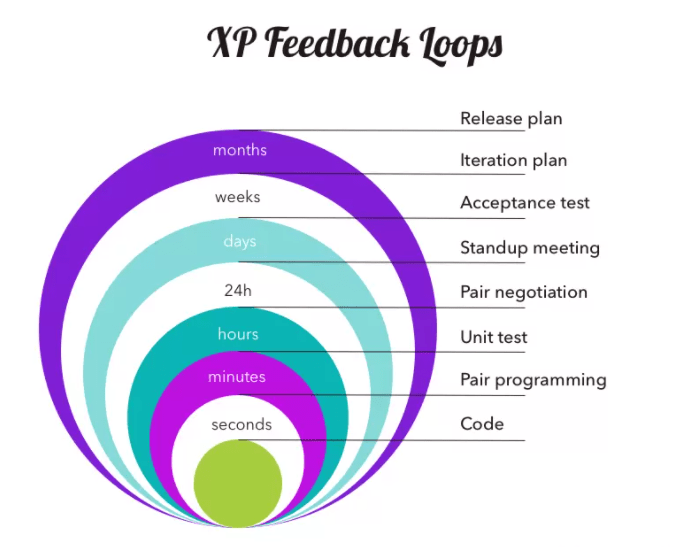
- ХP — is a set of practices for improving code as quickly as possible, e.g., code refactoring, and design simplification. The cycle usually lasts less than one week. It allows you to quickly create the first version and then deal with scaling up. It is suitable for your MVP, where code quality is important.
- Alpha and beta testing, which allows you to know what features need to be added, changed, or removed.
Basically, stage 9 is what the whole thing was about. During alpha testing, friends, family members, and acquaintances are involved in the process. If the internal test is successful, beta testing with the participation of outside users begins. One to two weeks is enough to collect the first feedback and move on to version upgrades. The number of cycles and the time frames depend on the peculiarities of the product. As a result, you can decide whether to go back to the first stage, continue working, or close the project.
A minimum viable product — is more than just testing an idea. It is the best way to get rid of the fear of failure. Thanks to testing, you can prevent the negative consequences that will appear when you launch a non-demanded service or software. Have you ever thought that companies whose services you use all the time - Groupon, Spotify, WhatsApp, Airbnb, Dropbox, Uber, Twitter - also started with an MVP? Isn't that the best proof that an MVP is the foundation for business promotion?






